Compacted Fill Dirt Calculator
Account for compaction factors to order the right amount of fill dirt. Calculate volume needed for foundations, driveways, and grading projects.
Pro Fill Dirt Calculator
Accurate estimates for Yards, Tons, & Compaction
Results
How to Calculate for Compacted Fill Dirt Calculator
The Formula
Calculate the compacted volume you need, then multiply by (1 + your compaction factor) to determine the loose cubic yards to order. Common factors: Clay 20-25%, Sand 10-15%, Mixed 15-20%.
Measure Accurately
Measure in feet. For depth, measure in inches and our tool handles the conversion (divide by 12).
Check Your Shape
Most compacted fill-dirt-calculator projects are rectangles. If irregular, break it into smaller shapes.
Add Compaction
Fill dirt shrinks 10-30% when compacted. Without adding extra material for this factor, you'll end up short on material, causing project delays and additional delivery costs.
Understanding Fill Dirt Compaction
Fill dirt compaction is the process of mechanically increasing soil density by reducing air pockets and voids within the material. When loose fill dirt is delivered to your site, it contains significant empty space between particles. Compaction removes this air, causing the material to settle and shrink in volume while gaining strength and stability.
The compaction process transforms loose, fluffy dirt into a dense, stable base capable of supporting structures, vehicles, and other loads. This transformation happens through the application of mechanical force using specialized equipment like plate compactors, vibratory rollers, or jumping jacks.
Understanding the three states of soil is essential. Bank Cubic Yards (BCY) refers to dirt in its natural, undisturbed state in the ground. Loose Cubic Yards (LCY) describes the expanded volume after excavation. Compacted Cubic Yards (CCY) represents the final installed volume after mechanical compaction.
Why Compaction Matters for Your Project
Proper compaction directly impacts your project's long-term success and structural integrity. Uncompacted or poorly compacted fill dirt will continue to settle over months or even years, leading to cracks in foundations, sunken driveways, uneven patios, and costly repairs.
Compacted fill dirt offers dramatically improved load-bearing capacity compared to loose material. A properly compacted base can support the weight of buildings, vehicles, and hardscaping without deforming or failing. This stability is particularly important for foundations, retaining wall backfill, and any surface that will carry loads.
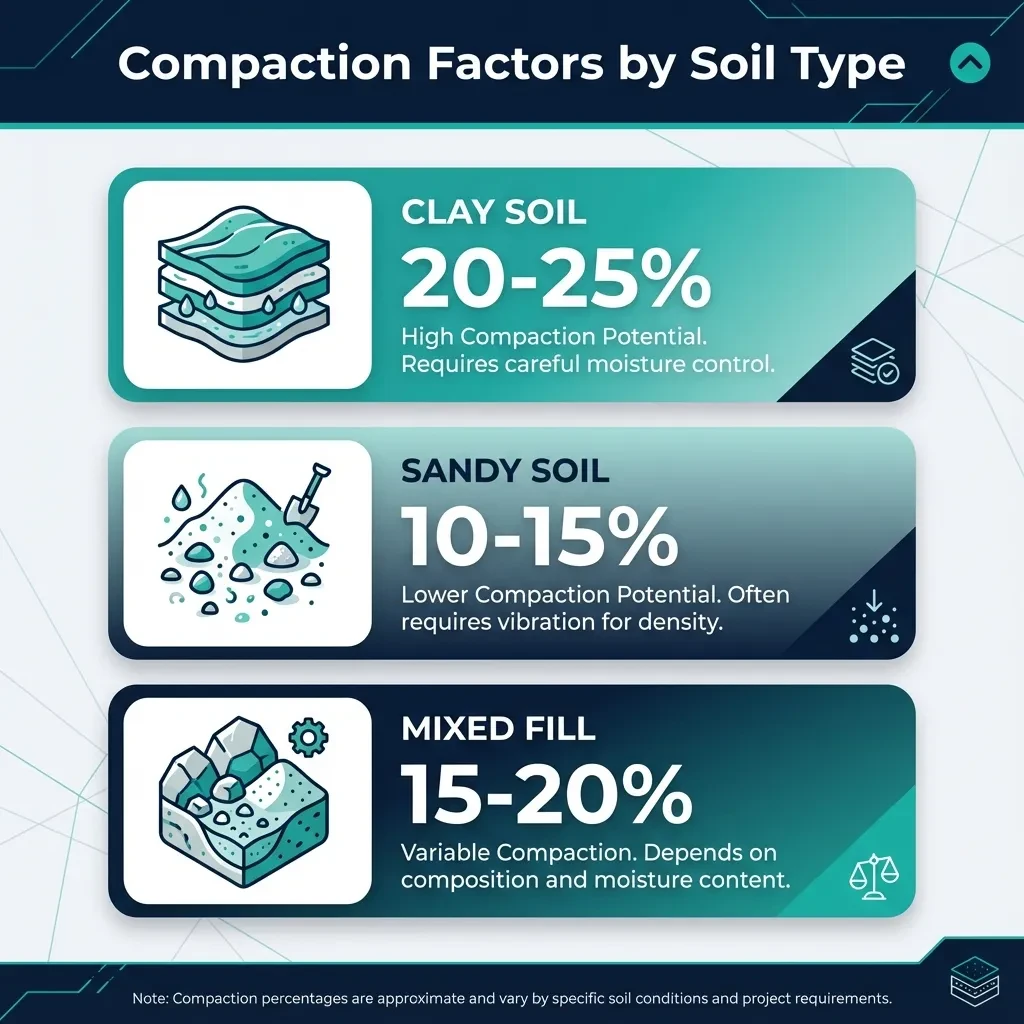
How Much Does Fill Dirt Compact?
Fill dirt typically compacts between 10% and 30% depending on its composition, moisture content, and the compaction method used. This means if you need 10 cubic yards of compacted fill, you'll actually need to order 11 to 13 cubic yards of loose material.
- Clay soils - generally compact at the higher end, around 20-25%
- Sandy soils - compact less dramatically, typically 10-15%
- Mixed fill dirt - the most common type, usually compacts around 15-20%
How to Calculate Fill Dirt with Compaction (Manual Method)
Basic Volume Calculation Formula
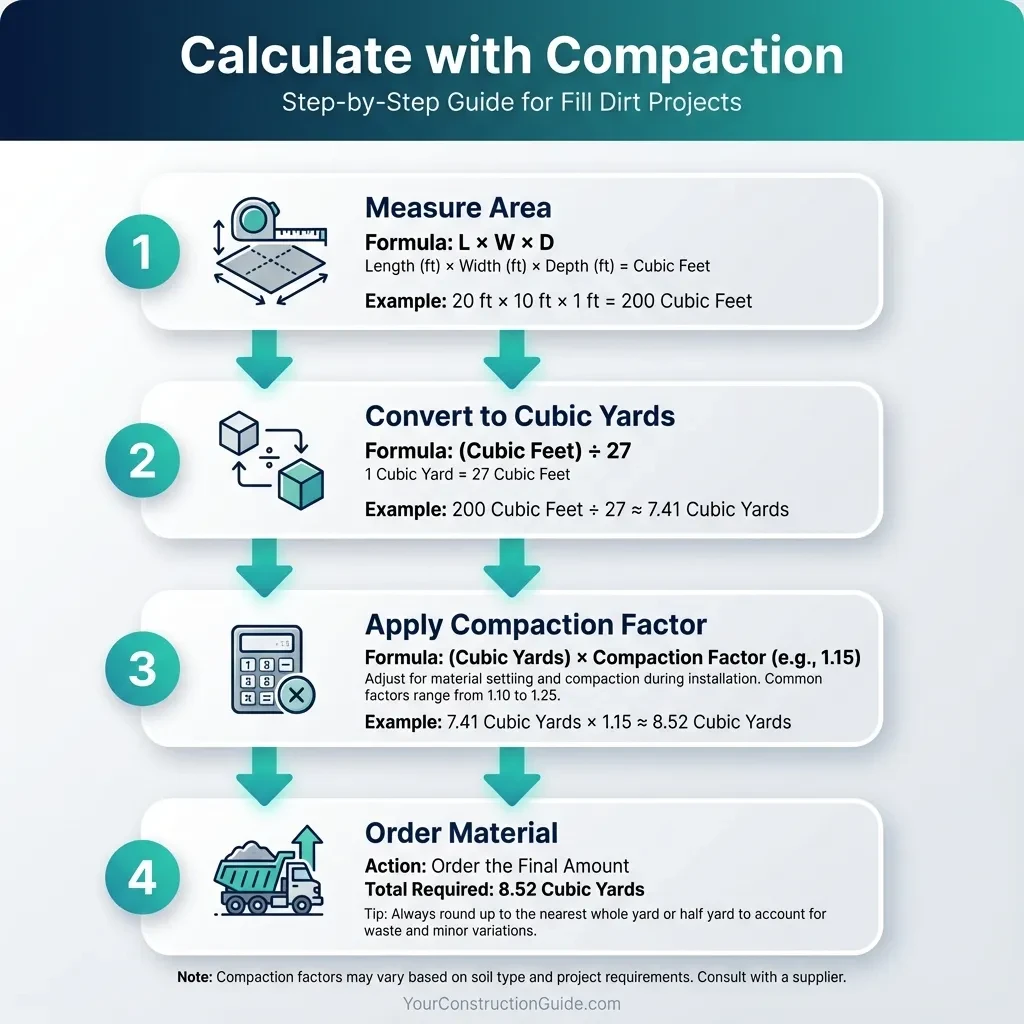
Understanding how to calculate fill dirt with compaction manually helps verify calculator results and build confidence in your ordering decisions. Start with the basic volume formula: Length × Width × Depth equals cubic feet.
Volume (cubic feet) = Length × Width × Depth
Cubic Yards = Cubic Feet ÷ 27
For example, if you're filling an area 30 feet long, 20 feet wide, and 2 feet deep, multiply 30 × 20 × 2 to get 1,200 cubic feet. Divide by 27 to get approximately 44.4 cubic yards of compacted fill needed.
Applying the Compaction Factor
Now apply your compaction factor to determine loose material requirements. The formula is: Compacted Volume × (1 + Compaction Percentage). If using a 15% compaction factor, calculate 44.4 × 1.15 to get 51.1 cubic yards of loose fill dirt to order.
Example Calculation:
- Area: 30 ft × 20 ft × 2 ft = 1,200 cubic feet
- Convert to yards: 1,200 ÷ 27 = 44.4 cubic yards (compacted)
- Apply 15% compaction: 44.4 × 1.15 = 51.1 cubic yards to order
Bank, Loose, and Compacted Cubic Yards Explained

Bank Cubic Yards (BCY)
Material in its natural, undisturbed state before excavation. This is the baseline measurement.
Loose Cubic Yards (LCY)
After excavation, soil expands 15-30%. This is what suppliers deliver to your site.
Compacted Cubic Yards (CCY)
Final installed volume after mechanical compaction. This is your target measurement.
This is the measurement you'll use when ordering fill dirt from suppliers. They quote prices in loose cubic yards because that's the volume their trucks deliver. A tandem-axle dump truck typically carries 12-15 loose cubic yards, while a triaxle truck hauls 18-20 loose cubic yards.
Proper Compaction Techniques
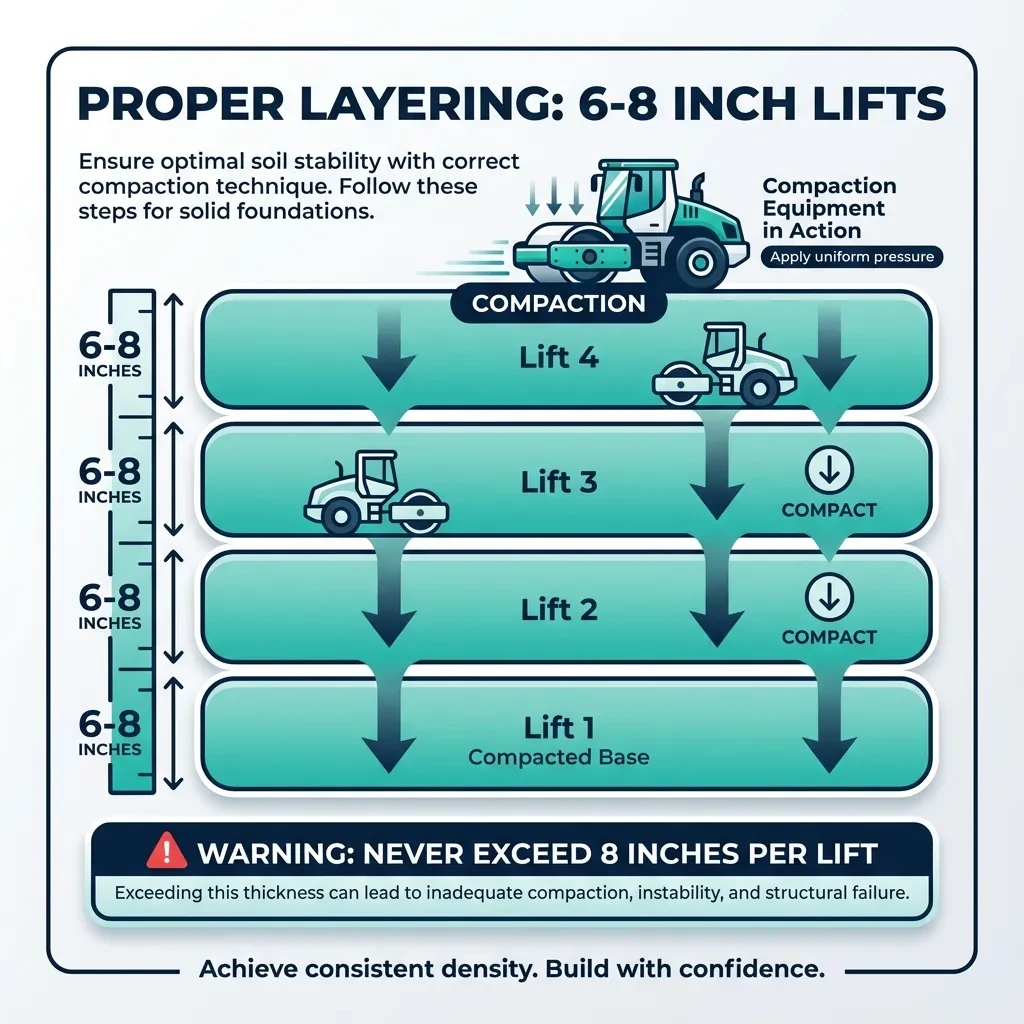
Layering and Lift Thickness
Proper layering is the cornerstone of effective compaction. Attempting to compact thick deposits of fill dirt leaves air pockets deep within the material that will settle over time, causing future problems. Industry best practice calls for lifts no thicker than 6-8 inches of loose material.
Spread this amount evenly across your project area, compact it thoroughly until no further densification occurs, then add the next lift. This progressive method ensures uniform density throughout the entire fill depth.
Equipment Selection

- Plate compactors - work well for small to medium projects (under 2,000 sq ft), $60-100/day rental
- Vibratory rollers - suit larger areas (over 2,000 sq ft), $150-300/day rental
- Jumping jacks - best for clay soils and confined spaces like trenches
Common Fill Dirt Compaction Mistakes

Underestimating compaction requirements
Ordering only compacted volume leaves you short
Using incorrect compaction factors
Clay needs higher factors than sand
Compacting layers too thick
Never exceed 8 inches per lift
Ignoring moisture content
Both too dry and too wet soil compact poorly
Skipping intermediate compaction
Each layer must be compacted before adding more
Not testing compaction results
Critical for structural applications
Rushing the compaction process
Multiple passes are required for proper density
Over-compacting sensitive areas
Can damage utilities and structures
Fill Dirt Calculator with Compaction Square Feet Applications
Foundation and Building Pad Projects
Foundation projects demand highly accurate compaction calculations. A 2,000 square foot building pad requiring 2 feet of fill needs approximately 148 cubic yards compacted. With a 20% compaction factor for structural fill, order 178 cubic yards of loose material.
Driveway Base Preparation
A standard 30×12 ft driveway with 6-inch base needs about 6.7 cubic yards compacted. With 18% compaction factor, order 8 cubic yards of loose fill. Compact in two 3-inch layers for uniform density. For foundation work, check our house pad calculator.
Landscaping and Grading
A 1,500 square foot yard section needing 4 inches of fill requires about 18.5 cubic yards compacted. With 12% light compaction, order 21 cubic yards. Avoid over-compacting the top layer for lawn establishment.
Estimating Costs with Compaction Included
Fill dirt prices vary by region, typically ranging from $10 to $40 per cubic yard for loose material delivered. Compaction factors directly affect your material budget. For a project requiring 50 compacted cubic yards with 20% compaction, you'll order 60 loose cubic yards. At $20 per cubic yard, material costs are $1,200.
Typical Cost Components:
- Material: $10-40 per loose cubic yard
- Delivery: $50-150 for local (20 miles), $2-5/mile beyond
- Equipment rental: Plate compactor $60-100/day, roller $150-300/day
- Professional labor: $30-60/hour
Explore More Calculators
Find more specialized tools for your dirt and material calculations on DirtMasters:
- Fill Dirt Calculator (Homepage) - General purpose cubic yard calculator
- All Calculators - Browse our complete collection
- Fill Dirt Cost Calculator - Estimate project costs
- Slope Calculator - Calculate for graded surfaces
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you calculate compacted fill dirt needed?
Calculate the volume you need in cubic yards (length × width × depth ÷ 27), then multiply by your compaction factor. For example, 20 cubic yards needing 15% compaction requires 20 × 1.15 = 23 cubic yards of loose fill.
What is a typical compaction factor for fill dirt?
Most fill dirt requires a 15-20% compaction factor. Clay soils compact more (20-25% factor), while sandy soils compact less (10-15% factor). The exact rate depends on soil composition and compaction method.
How do I convert square feet to cubic yards for fill dirt?
Multiply your square footage by depth in feet to get cubic feet, then divide by 27 to get cubic yards. For example, 1,000 square feet with 6 inches (0.5 feet) of depth equals 500 cubic feet, or about 18.5 cubic yards.
How thick should each layer of fill dirt be for compaction?
Limit each lift to 6-8 inches of loose material maximum. Thicker layers prevent compaction equipment from adequately densifying the entire depth, leaving soft spots that cause future settling.
Can I compact fill dirt without special equipment?
Hand tamping works for very small areas like post holes, but isn't practical for larger projects. Renting a plate compactor costs $60-100 per day and dramatically improves results while saving time.
What's the difference between loose and compacted volume?
Loose volume is the expanded state of excavated soil as delivered from suppliers. Compacted volume is the denser state after mechanical compaction removes air pockets. The difference is typically 10-30%.
How long does compacted fill dirt take to settle?
Properly compacted fill settles minimally, usually less than 1-2% over several months. Poorly compacted fill might settle 5-15% or more over years, causing structural problems.
Do I need to test fill dirt compaction?
Testing is essential for structural applications like foundations, retaining walls, or projects requiring building permits. General landscaping often doesn't require formal testing but it provides valuable verification.
What moisture level is best for compacting fill dirt?
Optimal moisture content is typically 10-15% for most soils. At this level, soil forms a ball when squeezed but doesn't leave much moisture on your hands. Both very dry and saturated soil compact poorly.
How many tons are in a cubic yard of compacted fill dirt?
Compacted fill dirt weighs approximately 1.8-2.2 tons per cubic yard depending on composition and moisture content. Use 2.0 tons per cubic yard as a general estimate for purchasing calculations.
Can you over-compact fill dirt?
While rare with standard residential equipment, over-compaction can occur with very heavy machinery, potentially breaking down soil structure. More commonly, excessive compaction near utilities or structures causes damage to those features.
What's the difference between bank, loose, and compacted cubic yards?
Bank cubic yards (BCY) is undisturbed natural soil. Loose cubic yards (LCY) is excavated, expanded material as delivered. Compacted cubic yards (CCY) is the final installed volume after mechanical compaction.
How do I calculate fill dirt for a driveway with compaction?
Measure driveway length × width × base depth to get cubic feet, divide by 27 for cubic yards, then multiply by your compaction factor (typically 1.15-1.20). A 30×12 ft driveway with 6-inch base needs about 8 cubic yards.
Is a plate compactor enough for fill dirt compaction?
Plate compactors handle most residential projects under 2,000 square feet effectively. For larger areas or heavy-duty applications, vibratory rollers provide faster coverage and greater compaction force.
How much does fill dirt shrink when compacted?
Fill dirt typically shrinks 10-30% from its loose volume when properly compacted. Clay-heavy soil shrinks more (20-30%), sandy soil shrinks less (10-15%), and mixed fill averages 15-20% shrinkage.