How Much Dirt to Fill a Raised Bed Calculator
Calculate the perfect soil volume for your raised garden beds. Get exact measurements, cost estimates, and expert soil mix recommendations.
Pro Fill Dirt Calculator
Accurate estimates for Yards, Tons, & Compaction
Results
How to Calculate for How Much Dirt to Fill a Raised Bed Calculator
The Formula
For a 4×8 raised bed that's 12 inches deep: 8 ft × 4 ft × 1 ft = 32 cubic feet. Add 15-20% for settling = 37-38 cubic feet needed.
Measure Accurately
Measure in feet. For depth, measure in inches and our tool handles the conversion (divide by 12).
Check Your Shape
Most how much-dirt-to-fill-a-raised-bed-calculator projects are rectangles. If irregular, break it into smaller shapes.
Add Compaction
Bagged soil costs $3-5/cubic foot while bulk costs $1-2/cubic foot. Accurate calculations save hundreds on larger beds. Adding 15-20% buffer prevents running short when soil settles.
Picture this: you've just built your dream raised garden bed, ready to grow fresh vegetables and herbs. You head to the garden center, guess how much soil you need, and end up making three more trips—or worse, you buy way too much and watch bags of expensive soil sit unused in your garage. Sound familiar?
Calculating the exact amount of dirt for your raised bed doesn't have to be a guessing game. Whether you're filling a small 4×4 herb garden or multiple large vegetable beds, knowing precisely how much soil you need saves you time, money, and backbreaking labor. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about using a how much dirt to fill a raised bed calculator, understanding soil depth requirements, choosing the right soil mix, and avoiding common mistakes that cost gardeners hundreds of dollars every season.
Understanding Raised Bed Soil Volume: The Basics
How Raised Bed Soil Calculators Work
At its core, a raised bed soil calculator uses a simple volume formula: Length × Width × Depth = Volume. But don't let the simplicity fool you—getting this calculation right is crucial for your gardening success and your wallet.
Every cubic foot of quality soil costs between $1 and $5, depending on whether you're buying bagged or bulk. For a standard 4×8×1 foot raised bed (32 cubic feet), that's potentially $32 to $160 worth of soil. If your measurements are off by just a few inches, you could waste significant money.
Pro tip: Always measure the interior dimensions of your raised bed. If your bed is 4 feet on the outside with 2-inch thick walls, your interior dimension is actually 3 feet 8 inches (or 3.67 feet). That difference adds up quickly.
Cubic Feet vs. Cubic Yards
Cubic Feet is standard for bagged soil. Cubic Yards is standard for bulk delivery. The relationship: 1 cubic yard = 27 cubic feet
Bagged Soil Cost
$3-5 per cubic foot
32 cu ft bed = $96-160
Bulk Delivery Cost
$1-2 per cubic foot
32 cu ft bed = $32-64
How Deep Should Your Raised Bed Soil Be?
One of the most common questions gardeners ask is: "How deep should my raised bed be?" The answer depends entirely on what you're growing.
Shallow-Rooted (6-8")
- • Lettuce, spinach, arugula
- • Radishes
- • Most herbs
- • Microgreens
Medium-Rooted (12-18")
- • Tomatoes, peppers
- • Carrots, beets
- • Cabbage, broccoli, kale
- • Beans, peas, cucumbers
This is the sweet spot for most vegetables!
Deep-Rooted (18-24"+)
- • Tomatoes (indeterminate)
- • Squash, pumpkins, melons
- • Asparagus, rhubarb
- • Artichokes
Don't Forget Watering Space
Leave 1-2 inches of space between the top of your soil and the rim of your raised bed. This prevents soil erosion when watering, gives room for mulch, and allows water to pool briefly for better penetration.
Step-by-Step: How to Calculate Dirt for Your Raised Bed
Measure Your Raised Bed Dimensions
Measure interior dimensions (inside wall to inside wall) for length, width, and depth.
Common mistake: Measuring exterior adds wall thickness, inflating your calculation by 10-15%!
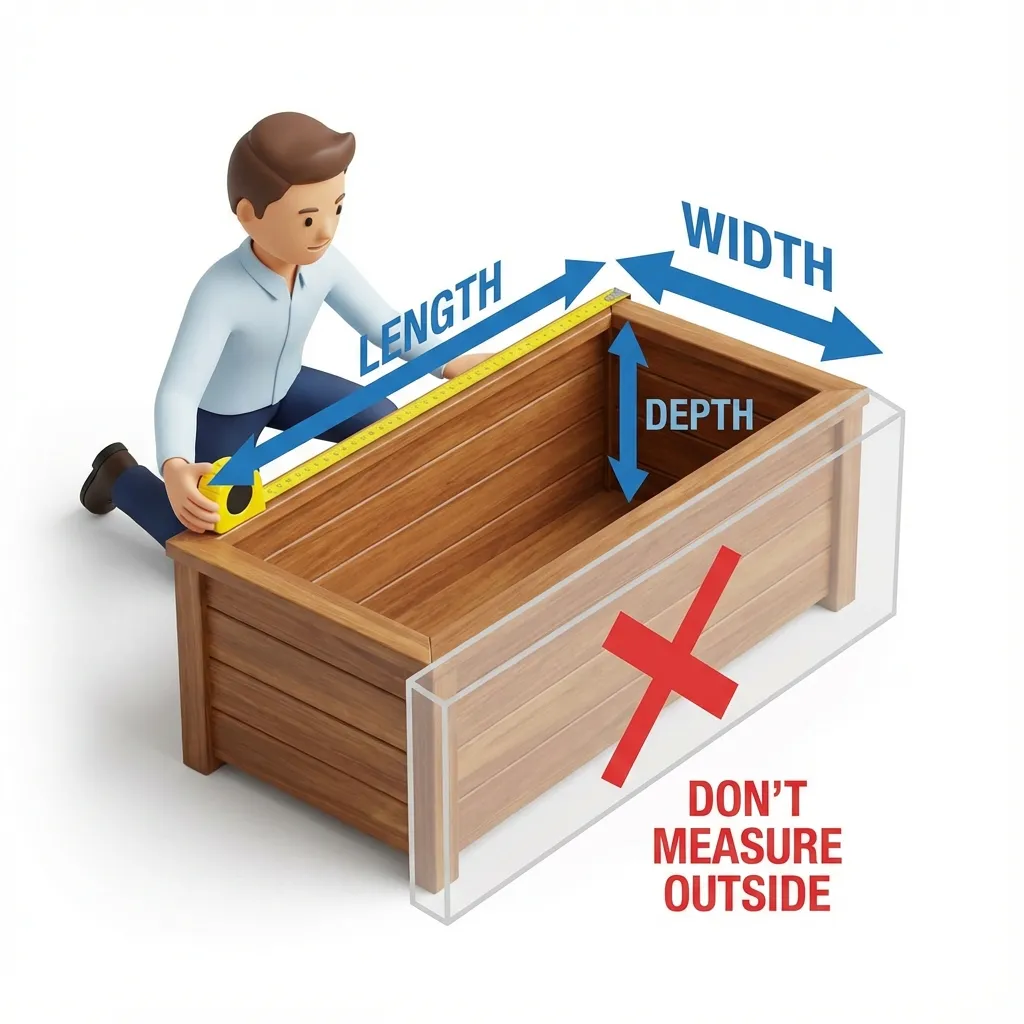
Multiply to Get Total Volume
Length × Width × Depth = Total Cubic Feet
Example: 8 ft × 4 ft × 1 ft = 32 cubic feet
Add 15-20% Extra for Soil Settling
Soil settles over time as air pockets collapse and organic matter decomposes.
32 cubic feet × 1.15 = 36.8 cubic feet (use 37)

Determine Bag Count or Bulk Amount
Convert to bags or cubic yards based on your purchasing method. Our cubic yards calculator makes this easy.
For Bags:
37 ÷ 2 = 19 bags (2 cu ft)
For Bulk:
37 ÷ 27 = 1.4 cubic yards
Best Soil Mix Ratios for Raised Beds
The quality of your soil mix matters just as much as the quantity. Never use 100% topsoil—it compacts heavily and lacks organic matter.
50/50 Mix (Budget-Friendly)
- • 50% topsoil
- • 50% compost
Best for: General vegetable gardening, tight budgets
Cost: ~$56 for 32 cu ft
Garden Betty's Mix
- • 50% topsoil
- • 30% compost
- • 20% organic matter
Best for: Heavy feeders, balanced performance
Cost: ~$43-53 for 32 cu ft
Mel's Mix (Square Foot)
- • 1/3 blended compost
- • 1/3 vermiculite
- • 1/3 peat moss/coco coir
Best for: Water conservation, intensive planting
Cost: ~$112 for 32 cu ft
40/40/20 Mix
- • 40% topsoil
- • 40% compost
- • 20% coarse sand/perlite
Best for: Rainy climates, excellent drainage
Cost: ~$54 for 32 cu ft
Bagged Soil vs. Bulk Delivery
When to Buy Bagged
- ✓ Small beds under 1 cubic yard
- ✓ Urban settings with limited delivery access
- ✓ Need specific branded products
- ✓ Immediate availability
Best for beds under 27 cubic feet
When to Order Bulk
- ✓ Large beds or multiple beds (1+ yards)
- ✓ Significant cost savings (50-70%)
- ✓ Less physical labor
- ✓ Environmentally friendly (no packaging)
Break-even point: ~1-1.5 cubic yards
Cost Comparison Example
For a 4×8×1 ft bed (32 cubic feet):
Bagged: $112-198
16-22 bags + heavy lifting
Bulk: $135
1.5 yards delivered + $75 fee
Money-Saving Tips
Make Your Own Compost
Reduce costs by 30-50% with homemade compost
Split Bulk Delivery
Share delivery fee with neighbors
Hugelkultur Method
Fill bottom with free logs and branches
Explore More Fill Dirt Resources
Conclusion: Getting Your Raised Bed Soil Right the First Time
Calculating how much dirt to fill a raised bed doesn't have to be complicated or stressful. By following the steps in this guide—measuring accurately, understanding your plants' depth needs, choosing the right soil mix, and accounting for settling—you'll get it right the first time and save yourself money, time, and frustration.

Key Takeaways:
- ✓ Always measure interior dimensions, not exterior
- ✓ Add 15-20% extra soil to account for settling
- ✓ Choose bulk delivery for beds over 1 cubic yard to save money
- ✓ Use a blended soil mix (never 100% topsoil) for best results
- ✓ Consider your plants' specific depth requirements
- ✓ Fill in fall for best results, or at least 2-4 weeks before planting
Whether you're filling one small herb bed or creating an entire raised bed vegetable garden, the how much dirt to fill a raised bed calculator makes the math simple. Combined with the knowledge you've gained from this guide, you're now fully equipped to create the perfect growing environment for your plants.
Happy gardening, and may your raised beds overflow with abundance!
Frequently Asked Questions
How much soil do I need for a 4×8 raised bed that's 12 inches deep?
You need 32 cubic feet of soil (8 ft × 4 ft × 1 ft). Add 15-20% for settling = 37-38 cubic feet total. This equals 1.4 cubic yards or about 19 bags of 2 cubic foot soil.
Can I use 100% compost in my raised bed?
Not recommended. Pure compost is too nutrient-rich and can burn plants. It also compacts heavily. Use compost as 30-50% of your mix, combined with topsoil and drainage amendments like perlite or sand.
What's the difference between topsoil and garden soil?
Topsoil is screened natural soil—inexpensive but dense. Garden soil is topsoil amended with compost and organic materials—better but pricier. Best value: buy topsoil and blend with compost yourself at 50/50 ratio.
How do I calculate soil for multiple raised beds?
Calculate each bed individually (L×W×D), then add all totals together. For three 4×8×1 ft beds: 32+32+32=96 cubic feet (3.6 cubic yards). Add 15-20% settling buffer.
Do I need to remove grass before placing a raised bed?
For beds 12+ inches deep with open bottoms, grass will die naturally and decompose. For shallower beds or persistent weeds like Bermuda grass, remove grass first or lay cardboard underneath.
How many 40-pound bags of soil equal one cubic yard?
A 40-lb bag typically contains 0.75 cubic feet. One cubic yard = 27 cubic feet, so you need 36 bags (27÷0.75=36). Always check bag labels for volume, not just weight.
Can I fill the bottom of my raised bed with sticks and leaves?
Yes! The Hugelkultur method uses logs and organic matter in the bottom 6-12 inches. As it decomposes, it retains water and releases nutrients while reducing soil costs by 30-50%. Best for deep beds (18+ inches).
What soil depth do tomatoes need in a raised bed?
Tomatoes need 12-18 inches. Determinate varieties work in 12 inches, indeterminate prefer 18 inches. If your bed sits on good native soil, roots extend beyond the bed, so 10-12 inches raised bed soil is sufficient.
Should I mix my soil components or layer them?
Both work. Mixing thoroughly creates uniform medium (more work). Layering is easier—add components in layers and let watering blend them over time. Most gardeners find layering works fine.
How often should I replace the soil in my raised beds?
With proper maintenance, never! Add 1-2 inches of compost annually, practice crop rotation, and test soil every 1-2 years. Well-maintained beds stay productive 10+ years.
What's the cheapest way to fill a large raised bed?
Use Hugelkultur (free logs/branches at bottom), order bulk delivery instead of bags (saves 50-70%), make your own compost, split delivery with neighbors, and use simple 50/50 topsoil/compost mix.
Can I use native soil from my yard in my raised bed mix?
Yes, if it's workable (not pure clay). Use it as 30-40% of mix with compost (40-50%) and drainage amendments (10-20%). Never use 100% native soil—always enhance with amendments.
How do I prevent my raised bed soil from compacting?
Use mix with 30-50% compost and 10-20% drainage amendments. Avoid walking on soil. Add 1-2 inches compost annually. Practice no-till gardening. Grow cover crops in fall.
What's the ideal pH for raised bed soil?
Most vegetables prefer pH 6.0-7.0 (slightly acidic to neutral). Test every 1-2 years. Add lime if too acidic, sulfur if too alkaline. Most compost-enriched mixes naturally fall in this range.
Do I need to add fertilizer to new raised bed soil?
If your mix is 40-50% quality compost, no fertilizer needed first season. For subsequent seasons, add 1-2 inches compost annually. Supplement with organic fertilizers for heavy feeders like tomatoes.